Blog
-
Let’s Go Over The Basics…The “Causes and Treatments” For Hearing Loss, Explained.
 7 Nov , 2016
7 Nov , 2016
Huh? What did you say? Can you please repeat that?”
If you find yourself straining to hear, you may have some degree of hearing loss, which can negatively impact your quality of life. Not only has hearing loss been linked to depression, it can also make one feel anxious, upset, or lonely.It’s natural to withdraw from others when one can’t follow what is being said at the dinner table. Friends and family may think the person is confused or even uncaring, when he or she is actually having trouble hearing.
Hearing loss can also be a safety issue, such as not hearing cars or ambulances on the road or smoke alarms in the home.
If you have difficulty hearing, help is available, including hearing aids, which are noninvasive. Other uncommon treatments may include cochlear implants or middle-ear surgery.
“As a board-certified audiologist, I feel each individual’s hearing needs should be uniquely addressed,” said Dr. Shoshana Richelson, a Southfield-based audiologist. “There are many factors that are involved which require expertise and skill. A board-certified audiologist can make sure that nothing is overlooked.”HOW DO I KNOW IF I HAVE HEARING LOSS?
See your doctor or audiologist if you:
• Have trouble hearing over the telephone.
• Find it hard to follow conversations when two or more people are talking.
• Often ask people to repeat what they are saying.
• Need to turn up the TV volume so loud that others complain.
• Have a problem hearing because of background noise.
• Think that others seem to mumble.
• Can’t understand when children speak to you.
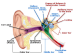
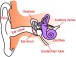
TYPES OF HEARING LOSS
Hearing loss can have many different causes. One common cause is presbycusis. Presbycusis (prez-bee-KYOO-sis) is a common type of hearing loss that develops gradually as a person ages. It often affects hearing in both ears. The degree of hearing loss varies from person to person. A common sign of early hearing loss is an impression that people around you are mumbling.
Loud noise is one of the most common causes of hearing loss. Noise from lawn mowers, concerts, motorcycles, firecrackers, or loud music can damage the inner ear and result in permanent hearing loss.
Importantly, noise-related hearing loss is preventable. Protect yourself by turning down the sound on your stereo, television, or headphones; move away from loud noise; or use earplugs or other ear protection.
Ear wax or fluid build-up can block sounds that are carried from the outer to inner ear. If wax blockage is a problem, try using mild treatments, such as mineral oil, baby oil, glycerin, or commercial ear drops, to soften the ear wax. You may need to see a physician to fully remove the earwax.
A punctured eardrum can also cause hearing loss. The eardrum can be damaged by infection, pressure, or putting objects in the ear, including cotton-tipped swabs.
See your doctor if you have pain or fluid draining from the ear. Viruses and bacteria, heart conditions, stroke, brain injuries, or tumors may affect your hearing. If you have hearing problems after starting a new medication, check with your doctor to see if another medicine can be used. Sudden deafness is a medical emergency that may be curable if treated in time. See a doctor right away.
Tinnitus (TIH-nih-tuhs or tih-NIE-tuhs) is described as a ringing or hissing noise in the ear. Tinnitus can go hand-in-hand with many types of hearing losses. It can also be a sign of other health problems, such as high blood pressure or allergies.
Often it is unclear what causes tinnitus, but there are ways to cope. Devices that create noise, such as a fan or a sound machine, are helpful. Half of those patients who wear hearing aids report a reduction in their tinnitus.
WHAT TREATMENT IS THERE FOR HEARING LOSS?
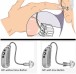
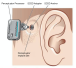
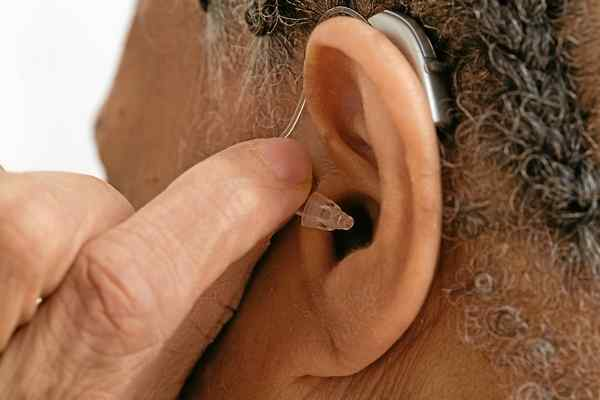
Hearing aids are the most common treatment for hearing loss. Hearing aids are electronic, battery-run devices that provide specific frequency amplification, as well as reduce background noise. There is exciting new technology in hearing aids that help reduce squealing and automatically switch programs in different listening situations.
Yet, hearing aids are only as good as the hearing care professional recommending and fitting them for you. It is important to choose an experienced hearing care professional to ensure that you are being fit with the optimal device for you.(At A Atlantic Hearing Aid, we have been at the same location, giving FREE hearing exams to the community, for over 45 years

Hearing aids should fit comfortably in your ears. Your hearing care professional should show you how to use your hearing aids and provide a follow-up plan for hearing aid checks.
Expect several visits with your hearing care professional throughout the years. Remember, when you buy a hearing aid, you are buying both a product and a service.
WORDS TO KNOW WHEN LOOKING FOR HEARING AIDS
• Digital hearing aids provide the wearer several features, such as background noise control.
• Telecoil refers to a magnetic coil in a hearing aid that helps you to hear when talking on the telephone or in buildings that have special sound systems.
• Induction loop systems can help you hear better in some public places, such a movie theaters and meeting places where microphones are used.
ASSISTIVE DEVICES
There are many products that can help you hear better.
• Telephone amplifying devices can make it easier to use the phone.
• TV and radio listening systems can let you hear the TV or radio without being bothered by background noise or needing to turn up the volume.
• Alert systems can work with doorbells, smoke detectors, and alarm clocks to send you visual signals or vibrations. For example, a flashing light could let you know someone is at the door or the phone is ringing, or a vibrating alarm clock under your pillow could wake you up in the morning.
All of these helpful products can be found at A Atlantic as well.
source: Next Avenue, By Debra Kaszubski,
Image Credit: Metro Creative Connection