Blog
-

‘Lancet’ Study Recommending Immediate Action for Dementia Prevention.
 16 Aug , 2017
16 Aug , 2017
‘Lancet’ Study Recommending Immediate Action for Dementia Prevention.
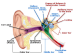
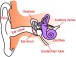
The Lancet report has received national press coverage for its particular focus on mitigating, as well as treating, dementia—a condition which affects about 47 million people globally, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
Members of the British and Irish Hearing Instrument Manufacturers Association (BIHIMA) welcome the recent study in The Lancet which recommends acting now, on dementia prevention and intervention and recognizes hearing loss as one of the most significant modifiable risk factors in developing dementia, BIHMA announced. BIHIMA represents the hearing instrument manufacturers of Britain and Ireland, working in partnership with other professional, trade, regulatory, and consumer organizations within the health care and charitable sectors.
It lists nine modifiable risk factors, with hearing loss at the top of the list. The study reports that eliminating hearing loss is highly relevant to reducing new cases of dementia.
In the announcement, BIHIMA says it thoroughly endorses this emphasis on prevention being better than cure and appreciates the report’s acknowledgement that this is an underinvested area of research. “To our knowledge, no systematic reviews have been done for hearing loss and incident dementia,” the report says, and “recognition of hearing loss as a risk factor for dementia is relatively new and has not been included in previous calculations of PAF [population attributable fractions], nor has it been a priority in the management of those at risk of cognitive impairment.”
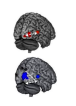
The report also acknowledges that there is still much work to be done to understand exactly why hearing loss can lead to dementia. It suggests that it “might add to the cognitive load of a vulnerable brain leading to changes in the brain, or lead to social disengagement or depression and accelerated atrophy, all of which could contribute to accelerated cognitive decline” but these conclusions also require further research.
According to BIHIMA, the report concedes that there is a lack of research into the role of hearing technology in the prevention of dementia: it is “not yet established,” it says, “whether correction, such as hearing aids, can prevent or delay the onset.” BIHIMA is concerned that this is an area that continues to be underfunded and underresearched and calls for further expedient investigation.
BIHIMA feels that dementia is one of the most pressing global health and social care challenges of the 21stcentury.
“There should be no time wasted when it comes to quantifying the vital role hearing technology could play in managing it,” said BIHIMA Chairman Paul Surridge in the announcement.
Source: BIHIMA, The Lancet
Image credit: Deposit photos